MIPS VM
Ziren is a verifiable computation infrastructure based on the MIPS32, specifically designed to provide zero-knowledge proof generation for programs written in Rust. This enhances project auditing and the efficiency of security verification. Focusing on the extensive design experience of MIPS, Ziren adopts the MIPS32r2 instruction set. MIPS VM, one of the core components of Ziren, is the execution framework of MIPS32r2 instructions. Below we will briefly introduce the advantages of MIPS32r2 over RV32IM and the execution flow of MIPS VM.
Advantages of MIPS32r2 over RV32IM
1. MIPS32r2 is more consistent and offers more complex opcodes
- The J/JAL instructions support jump ranges of up to 256MiB, offering greater flexibility for large-scale data processing and complex control flow scenarios.
- MIPS32r2 has rich set of bit manipulation instructions and additional conditional move instructions (such as MOVZ and MOVN) that ensure precise data handling.
- MIPS32r2 has integer multiply-add/sub instructions, which can improve arithmetic computation efficiency.
- MIPS32r2 has SEH and SEB sign extension instructions, which make it very convenient to perform sign extension operations on char and short type data.
2. MIPS32r2 has a more established ecosystem
- All instructions in MIPS32r2, as a whole, have been very mature and widely used for more than 20 years. There will be no compatibility issues between ISA modules. And there will be no turmoil caused by manufacturer disputes.
- MIPS has been successfully applied to Optimism’s Fraud Proof VM
Execution Flow of MIPS VM
The execution flow of MIPS VM is as follows:
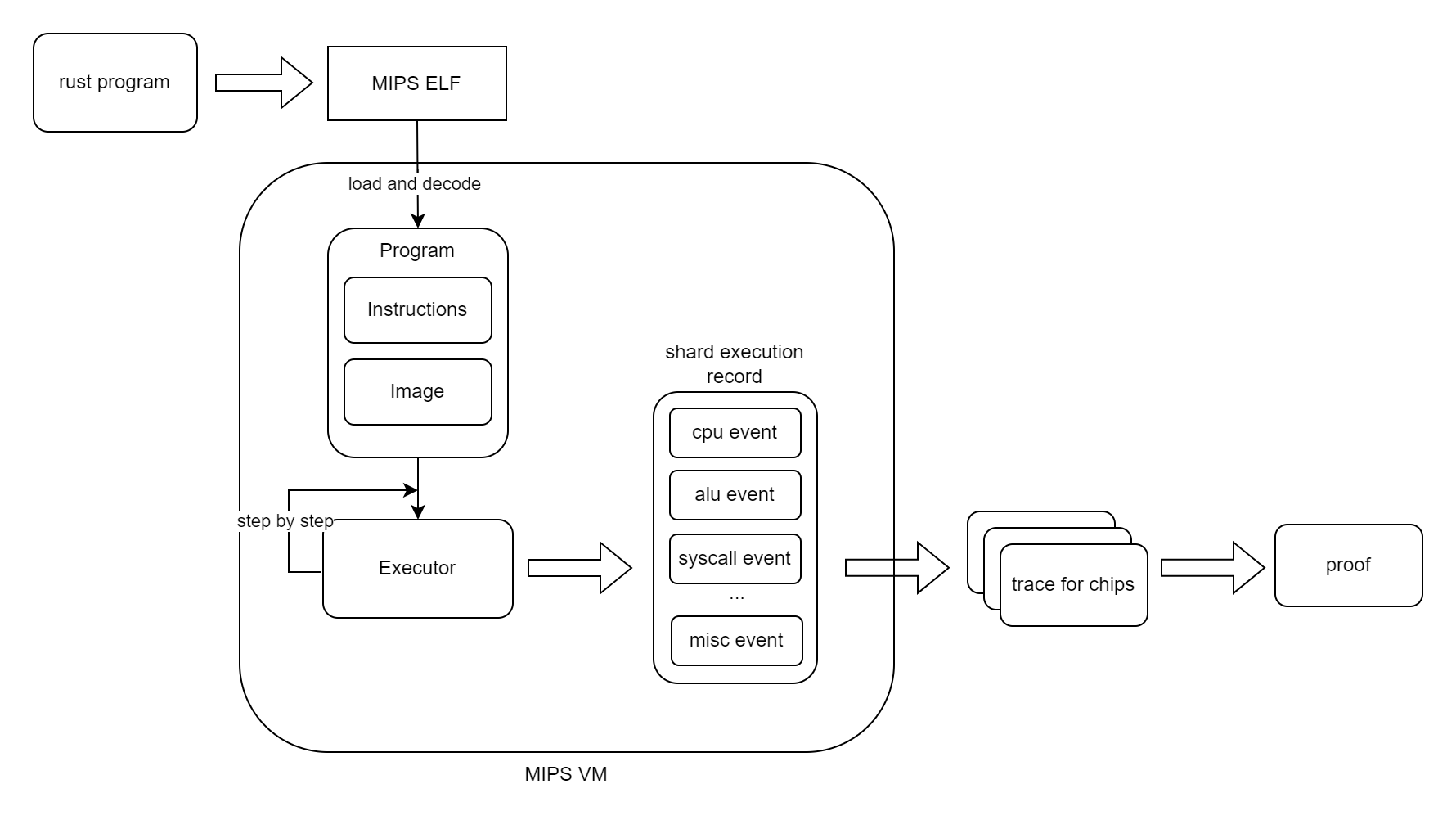 Before the execution process of MIPS VM, a Rust program written by the developer is first transformed by a dedicated compiler into the MIPS instruction set, generating a corresponding ELF binary file. This process accurately maps the high-level logic of the program to low-level instructions, laying a solid foundation for subsequent verification.
Before the execution process of MIPS VM, a Rust program written by the developer is first transformed by a dedicated compiler into the MIPS instruction set, generating a corresponding ELF binary file. This process accurately maps the high-level logic of the program to low-level instructions, laying a solid foundation for subsequent verification.
MIPS VM employs a specially designed executor to simulate the execution of the ELF file:
- First,the ELF code is loaded into Program, where all data is loaded into the memory image, and all the code is decoded and added into the Instruction List.
- Then, MIPS VM executes the Instruction and update the ISA states step by step, which is started from the entry point of the ELF and ended with exit condition is triggered. A complete execution record with different type of events is recorded in this process. The whole program will be divided into several shards based on the shape of the execution record.
After the execution process of MIPS VM, the execution record will be used by the prover to generate zero-knowledge proof:
- The events recorded in execution record will be used to generate different traces by different chips.
- This traces serve as the core data for generating the zero-knowledge proof, ensuring that the proof accurately reflects the real execution of the compiled program.
Memory Layout for guest program
The memory layout for guest program is controlled by VM, runtime and toolchain.
Rust guest program
Two kinds of allocators are provided to rust guest program
- bump allocator: both normal memory and program I/O is allocated from the heap. And the heap address is always increased and cannot be reused.
| Section | Start | Size | Access | Controlled-by |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| registers | 0x00 | 36 | rw | VM |
| Stack | 0x7f000000 | (stack grows down) | rw | runtime |
| Code | ||||
| .text | .text size | ro | toolchain | |
| .rodata | .rodata size | ro | toolchain | |
| .eh_frame | .eh_frame size | ro | toolchain | |
| .bss | .bss size | ro | toolchain | |
| Heap (contains program I/O) | _end | 0x7f000000 - _end | rw | runtime |
- embedded allocator: Program I/O address space is reserved and split from heap address space. A TLS heap is used for heap management.
| Section | Start | Size | Access | Controlled-by |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| registers | 0x00 | 36 | rw | VM |
| Stack | 0x7f000000 | (stack grows down) | rw | runtime |
| Code | ||||
| .text | .text size | ro | toolchain | |
| .rodata | .rodata size | ro | toolchain | |
| .eh_frame | .eh_frame size | ro | toolchain | |
| .bss | .bss size | ro | toolchain | |
| Program I/O | 0x3f000000 | 0x40000000 | rw | runtime |
| Heap | _end | 0x3f000000 - _end | rw | runtime |
Go guest program
Go guest program is similar to embedded-mode rust guest program, except that the initial args is set by VM at the top of the stack. The memory layout is as follows:
| Section | Start | Size | Access | Controlled-by |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| registers | 0x00 | 36 | rw | VM |
| Stack | 0x7f000000 | (stack grows down) | rw | runtime |
| Initial args | 0x7effc000 | 0x4000 | ro | VM |
| Code | ||||
| .text | .text size | ro | toolchain | |
| .rodata | .rodata size | ro | toolchain | |
| .eh_frame | .eh_frame size | ro | toolchain | |
| .bss | .bss size | ro | toolchain | |
| Program I/O | 0x3f000000 | 0x40000000 | rw | runtime |
| Heap | _end | 0x3f000000 - _end | rw | runtime |